Install Subversion with Web Access on Ubuntu | Guide

Installing Subversion with Apache Module for Network Access
This guide details the installation of Subversion utilizing the Apache module, enabling access from systems across a public network. For heightened security, consider employing svnserve+ssh, though this method falls outside the scope of this document.
Installation Process
Begin by opening a terminal and executing the following command to install the necessary packages:
sudo apt-get install subversion libapache2-svn
We will establish the Subversion repository within the /svn directory. However, selecting a location with ample storage capacity is recommended.
sudo svnadmin create /svn
Configuring the Apache Module
Next, the configuration file for the Subversion WebDAV module requires modification. Feel free to utilize your preferred text editor.
sudo gedit /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dav_svn.conf
The element within the configuration file defines the root directory from which Subversion will be accessible. For example: http://www.server.com/svn
<location></location>
Ensure the DAV line is uncommented to activate the WebDAV module.
# Uncomment this to enable the repository,
DAV svn
The SVNPath line must correspond to the directory where you created the repository using the svnadmin command.
# Set this to the path to your repository
SVNPath /svn
Authentication Setup
The subsequent section allows for the activation of authentication. Note that this provides basic authentication and should not be considered a highly secure solution. The password file will be located as specified by the AuthUserFile setting, typically remaining at its default location.
# Uncomment the following 3 lines to enable Basic Authentication
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Subversion Repository"
AuthUserFile /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd
To create a user account for the repository, employ the following command:
sudo htpasswd2 -cm /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd
The -c option should only be used during the initial user creation. Subsequent users should be added using the -m option, which encrypts passwords using MD5 without recreating the file. For instance:
sudo htpasswd2 -cm /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd geek
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user geek
Restarting Apache
Restart the Apache service by executing this command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Finalizing Access Control
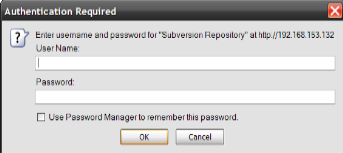
Accessing http://www.server.com/svn in your web browser should now reveal the repository with anonymous read access. Commit access will require valid credentials. To enforce authentication for all access, including read operations, add the following line immediately after the AuthUserFile line. Remember to restart Apache after making this change.
Require valid-user
Refreshing your browser will then prompt you for your username and password.
You have now successfully configured a functional Subversion server!